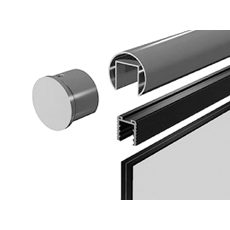
Baluster:
A vertical column used to support a railing on top and/or glass panels to the side of it.
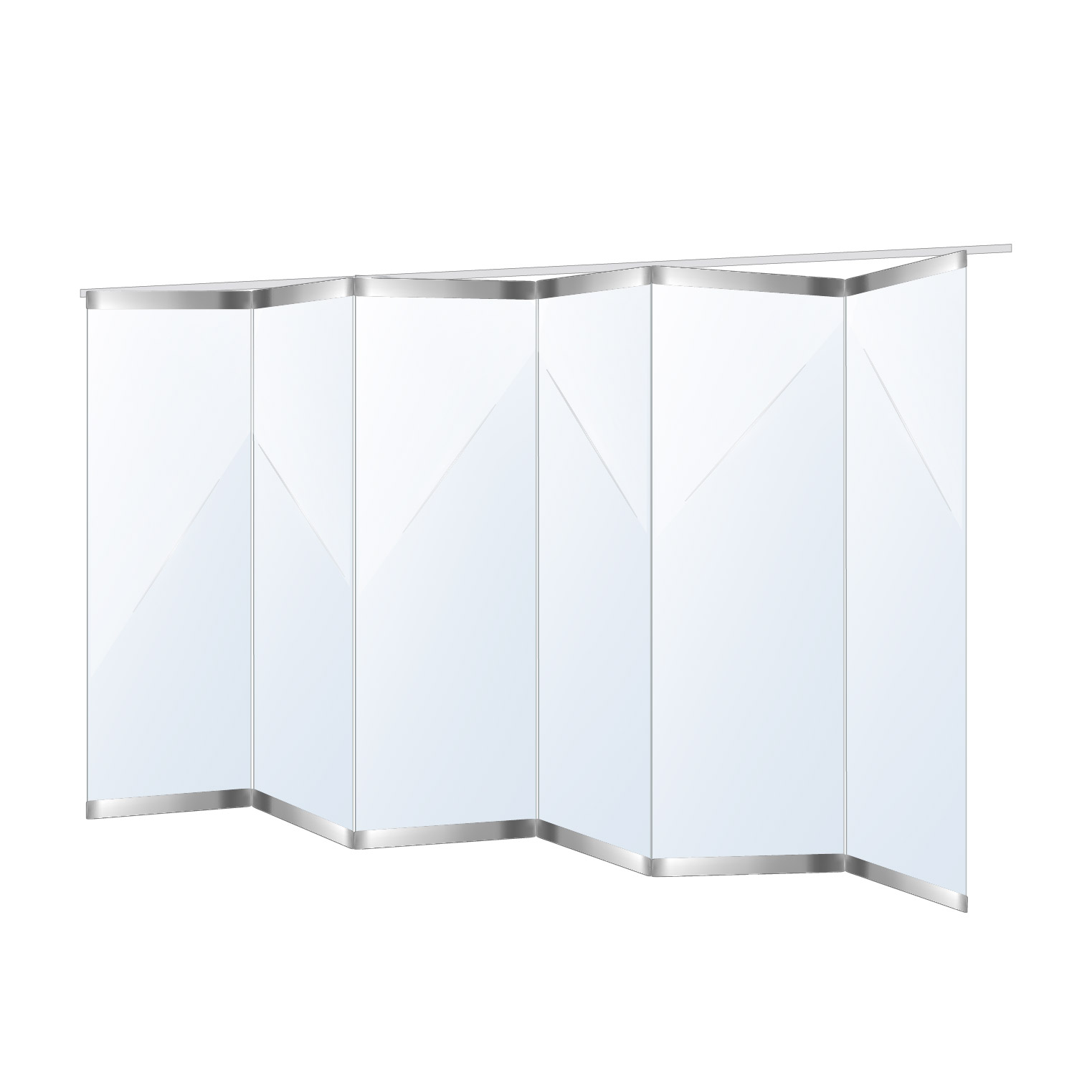
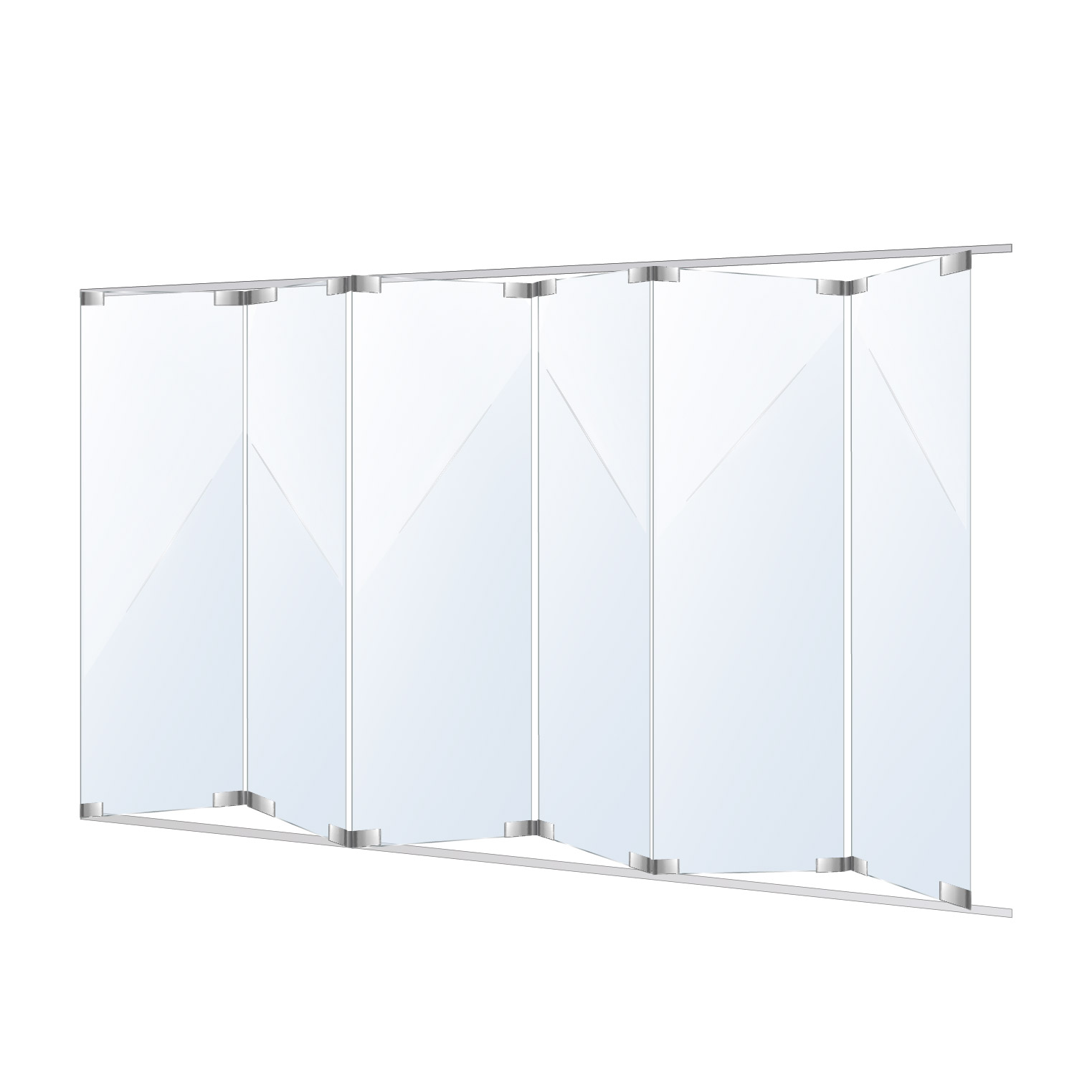
Balustrade:
A form of divide and/or protection from fall which is often used for safety and decoration on staircases, balconies, decks, or terraces.
An advanced design tool that allows users to create and customise balustrades using a drag-and-drop interface, complete with 3D visualisations and detailed specifications.
Base Rail:
The horizontal component at the bottom of a frameless balustrade system which supports the glass, ensuring structural integrity.
Cladding:
Only used when using a side fixed frameless balustrading, its purpose is to hide the fixings within the system.
Code Compliance:
Adherence to local building codes and safety regulations for balustrade design and installation, ensuring that all aspects meet legal and safety standards.
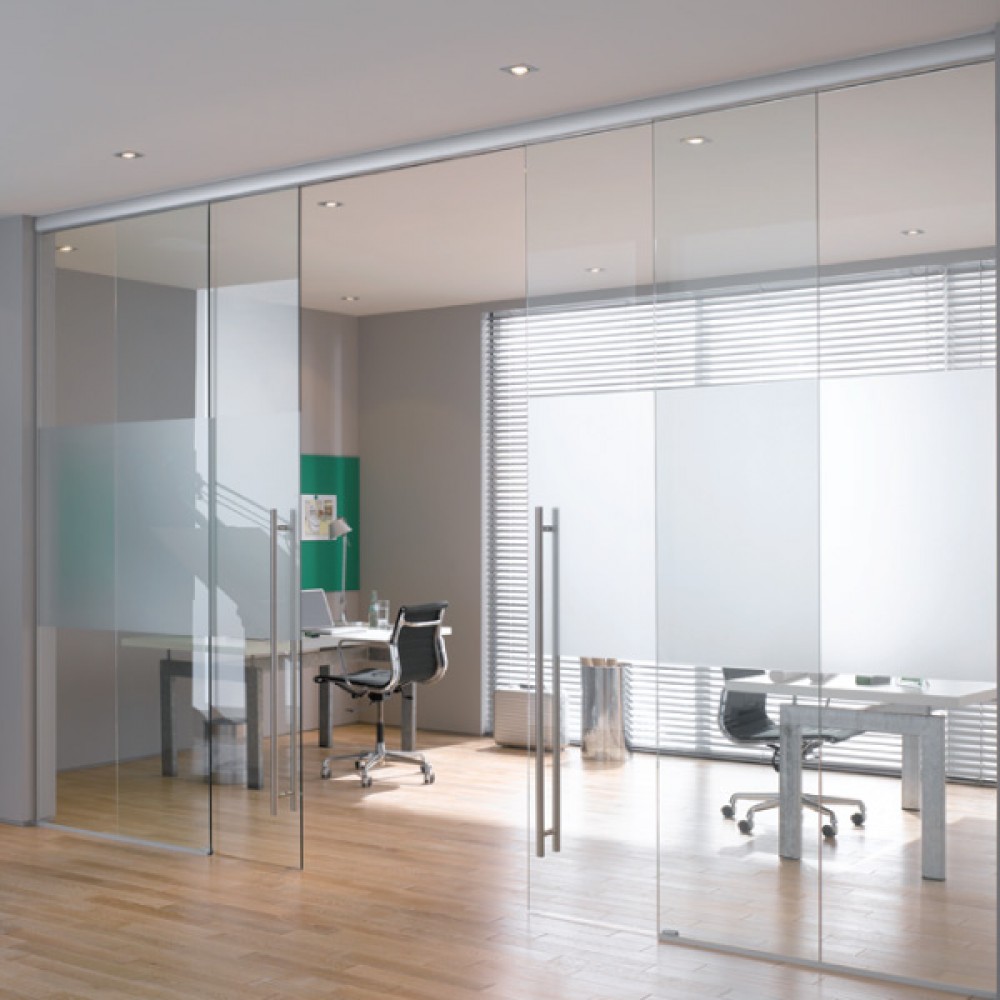
Crystal View:
A type of balustrade system that features clear, frameless glass panels, providing an unobstructed view and a sleek aesthetic.
EaziRail Alu:
An aluminium balustrade system known for its lightweight and durable properties, often used for modern and contemporary design applications.
Fall Protection:
Balustrade systems are installed to prevent falls or accidents at the edges of balconies, stairs, or other elevated areas
Components such as brackets, connectors, or fasteners are used to assemble and secure various parts of a balustrade system.
Glass Panels:
Flat, transparent or translucent sheets of glass are used in balustrades to provide a clear view while maintaining safety and security.
Handrail:
The top horizontal or sloped rail of a balustrade, designed for gripping and providing support, is typically installed at an appropriate height for safety.
Load-Bearing Capacity:
The maximum weight or force that a balustrade system can support without failing which is important for ensuring safety and compliance with standards.
Sometimes known as standoffs or buttons, these components are used to attach glass panels to a structure providing a clean and minimalistic look.
POSIglaze:
A type of balustrade system that features clear, frameless glass panels, providing an unobstructed view and a sleek aesthetic.
Railing Cap:
A decorative and protective cover placed on top of a balustrade post or to the edge of a handrail, providing a finished look.
Render:
A detailed, realistic visual representation of a design, generated by the software to show how the final balustrade will appear in its intended environment.
Safety Glass:
Glass that has been treated or laminated to increase its strength and reduce the risk of breakage or injury in the event of impact.
Seamless Integration:
The ability of different design tools or systems to work together without disruptions, ensuring a smooth flow of data and consistent results.
Spigots:
Stainless steel or aluminium fittings are used to support glass panels in a balustrade system. They are fixed to the floor or base and hold the glass in place.
Stainless Steel Finish:
A type of metal finish used for balustrade components, known for its durability, corrosion resistance, and sleek, modern appearance.
Structural Integrity:
The ability of a balustrade system to maintain its shape and support loads without failure. It is essential for ensuring safety and durability.
Uplift:
The upward force exerted on a balustrade system, is particularly important in high-wind areas, affects the choice of materials and design for stability.
Welded Joints:
Connections between metal components that are fused together using welding techniques, provide strong and durable joins in balustrade systems.
Workflows:
The sequence of processes or tasks involved in designing, fabricating, and installing a balustrade, is optimised for efficiency and accuracy.